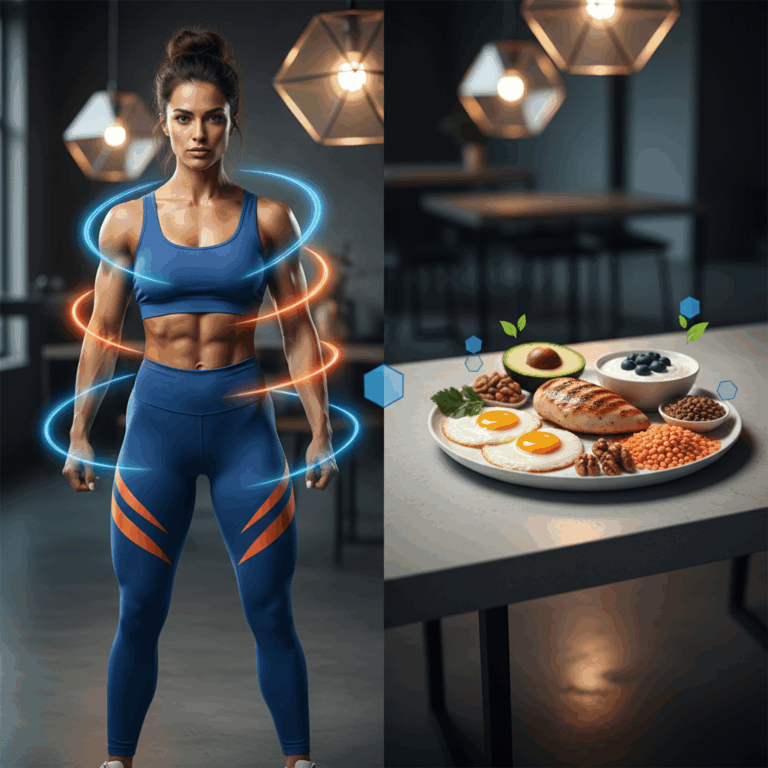
Role of Protein in Muscle Building
Protein is crucial for muscle development, providing the essential building blocks necessary for repairing and growing muscle tissue after exercise. This process supports a toned and strong physique, valued in both fitness and aesthetics.
During strength training, muscle fibers experience microscopic damage. Protein supplies amino acids that repair these fibers, promoting hypertrophy, which increases muscle size and definition over time, enhancing overall body composition.
Consuming adequate protein daily, combined with physical activity, accelerates muscle recovery and growth, making it a cornerstone of effective muscle building and maintenance.
Protein’s Function in Muscle Repair and Growth
Exercise causes small tears in muscle fibers, and protein provides the necessary amino acids to mend these micro-injuries. This repair is fundamental for muscle growth and strength gains.
The hypertrophy process depends heavily on protein availability, as it rebuilds damaged tissue stronger and larger. Without sufficient protein, muscle growth and recovery are impaired.
Optimal protein intake enhances both muscle repair speed and quality, allowing consistent progress in fitness routines and improved physical performance.
Sources of High-Quality Protein
High-quality protein sources include eggs, chicken breast, fish, Greek yogurt, lean meats, soy, and cottage cheese. These foods offer complete amino acid profiles essential for muscle health.
They also provide additional nutrients like B vitamins, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids, which support metabolic functions important for muscle energy and repair.
Regular consumption of these protein-rich foods ensures a balanced nutrient intake, aiding in effective muscle building and maintaining overall fitness.
Protein’s Impact on Body Composition
Protein significantly influences body composition by supporting fat loss while preserving and building lean muscle mass, crucial for a toned and athletic look.
Its ability to enhance satiety helps regulate appetite and reduce calorie intake, aiding weight management and contributing to a leaner physique with better muscle definition.
Incorporating sufficient protein into the diet, especially alongside exercise, supports fat reduction and muscle maintenance for an improved body shape and metabolism.
Protein and Satiety for Weight Management
High-protein meals increase feelings of fullness, helping to control hunger and reduce overall calorie consumption throughout the day, promoting effective weight management.
This satiety effect is linked to protein’s impact on hormones that regulate appetite, making it a valuable tool for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing overeating.
By reducing hunger, protein supports consistent dietary adherence and limits fat gain while preserving muscle during weight loss efforts.
Reduction of Body Fat and Muscle Definition
Protein intake supports fat loss by boosting metabolism through the higher energy cost of digesting it and helping maintain muscle mass during calorie deficits.
Preserving muscle while reducing body fat enhances muscle definition and creates a more sculpted and toned appearance, desired in fitness and fashion.
This dual effect of fat reduction and muscle retention is key to achieving a lean physique with visible muscle contours and improved overall aesthetics.
Essential Nutrients Supporting Muscle Metabolism
Besides protein, many rich sources provide key nutrients such as B vitamins, iron, and omega-3s, essential for efficient muscle metabolism and energy production.
These nutrients support muscle repair, oxygen transport, and reduce inflammation, optimizing recovery and muscle growth when combined with protein intake.
A balanced intake of protein and these nutrients enhances muscle function and definition, contributing to better physical performance and body composition.
Benefits of Protein for Fitness Performance
Protein plays a vital role in boosting fitness performance by enhancing muscle growth and increasing strength. It supports not only physical power but also endurance during workouts.
Consuming adequate protein ensures muscles recover faster and become stronger, allowing for more intense and frequent training sessions. This leads to continuous improvement in fitness levels.
Additionally, protein supports energy metabolism and muscle repair processes, which are essential for sustained athletic performance and reduced injury risk.
Increased Muscle Mass and Strength
Protein intake is directly linked to increased muscle mass and strength gains. Amino acids from protein help repair muscle fibers damaged during exercise, promoting hypertrophy.
Stronger muscles improve overall fitness capacity, enabling higher workloads, better balance, and enhanced power outputs in training and daily activities.
Ensuring sufficient protein intake post-workout accelerates muscle rebuilding, allowing athletes to make steady strength progress and physical adaptations.
Regular consumption of high-quality protein supports consistent muscle development, making strength gains more sustainable and noticeable.
Enhanced Physical Performance and Recovery
Protein facilitates quicker recovery by reducing muscle soreness and inflammation, enabling athletes to train more effectively with less downtime.
Improved recovery translates into enhanced physical performance, as muscles regain function and energy stores more rapidly after exercise.
Protein also supports the immune system and overall health, which are critical for maintaining high performance levels over time.
Proper protein timing and distribution throughout the day maximize its benefits for endurance, strength, and recovery, contributing to long-term fitness success.
Protein’s Influence on Fashion and Aesthetics
The integration of eiwit intake in fitness routines significantly shapes body aesthetics, aligning closely with contemporary fashion standards. A well-defined physique reflects discipline and health, which the fashion industry increasingly celebrates.
Fashion trends emphasize a toned and sculpted body, often achieved through muscle building supported by adequate protein consumption. This connection highlights how nutrition influences not only fitness but also the visual appeal in sartorial choices.
Protein fuels muscle growth and fat reduction, essential for attaining the sleek, athletic body types favored in modern fashion and media. This makes protein a critical element for those seeking both fitness and style goals.
Correlation Between Toned Physique and Fashion Trends
Modern fashion trends increasingly embrace athletic and toned bodies, reflecting a shift towards health-conscious aesthetics. This change aligns with the visible results of optimized protein intake and fitness training.
The rise of athleisure wear and form-fitting clothing highlights muscles and body contours, promoting a silhouette achievable through muscle definition supported by protein intake.
Models and influencers often showcase sculpted physiques, which signal strength and wellness, creating aspirational ideals that drive consumer behavior toward fitness and protein-rich diets.
Protein and Visual Appeal in Modern Fitness Culture
In fitness culture, protein is synonymous with physical enhancement, supporting not only muscle size but also the clarity of muscle tone that contributes to a visually appealing body.
High-protein diets combined with resistance training develop a firm, youthful appearance prized in fitness communities and social media, reinforcing protein’s role in aesthetic success.
Interesting Insight: Protein’s Role Beyond Muscle
Protein also supports skin, hair, and nail health, improving overall appearance. Collagen, a protein, contributes to skin elasticity, linking dietary habits to beauty outcomes viewed in fitness and fashion culture.
This holistic appeal extends protein’s influence beyond muscles, making it a vital nutrient for those aiming for comprehensive aesthetic enhancement in today’s fitness-focused lifestyle.